Protecting the Customer Data Lifecycle for Insurance
A leading insurance provider partnered with Agile Lab to embed GDPR compliance directly into its modern data lake architecture. By implementing automated classification, encryption, and masking of sensitive data, the company ensured secure handling of personally identifiable information (PII) while enabling safe and efficient data consumption across business functions.
Customer Context
In the highly regulated insurance sector, managing large volumes of sensitive customer data presents both operational and compliance challenges. Our client needed to modernize its data architecture to ensure GDPR compliance while continuing to support advanced analytics and day-to-day operations. With personally identifiable information spread across multiple systems, the insurer sought a scalable approach to protect customer data, reduce compliance risks, and provide analysts with secure, development-ready datasets without exposing critical information.
The Challenge
Modern data lakes are designed to store, process, and analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, often containing personally identifiable information (PII). However, with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in place, organizations must ensure that data privacy, security, and governance principles are embedded into the architecture.
This challenge required a comprehensive, scalable, and automated approach to meet the GDPR requirements such as:
- Data minimization – store only the necessary data, reduce exposure
- Right To Be Forgotten (RTBF) – ensure complete and verifiable deletion of user data upon request
- Data privacy & governance – implement strong access controls, encryption
- Auditing & handling massive and sensitive datasets – so track and manage efficiently PII across a large-scale data lake
The Solution: A Step Function Orchestrating Masking Jobs
The customer collected and processed personally identifiable information (PII), including names, addresses, phone numbers, and other sensitive details. To ensure compliance and mitigate risks, this data needed to be classified and tagged across all storage layers by means of a solution that copied the data in a highly restricted and secure environment to an environment with low restrictions after the secure encryption of sensitive information.
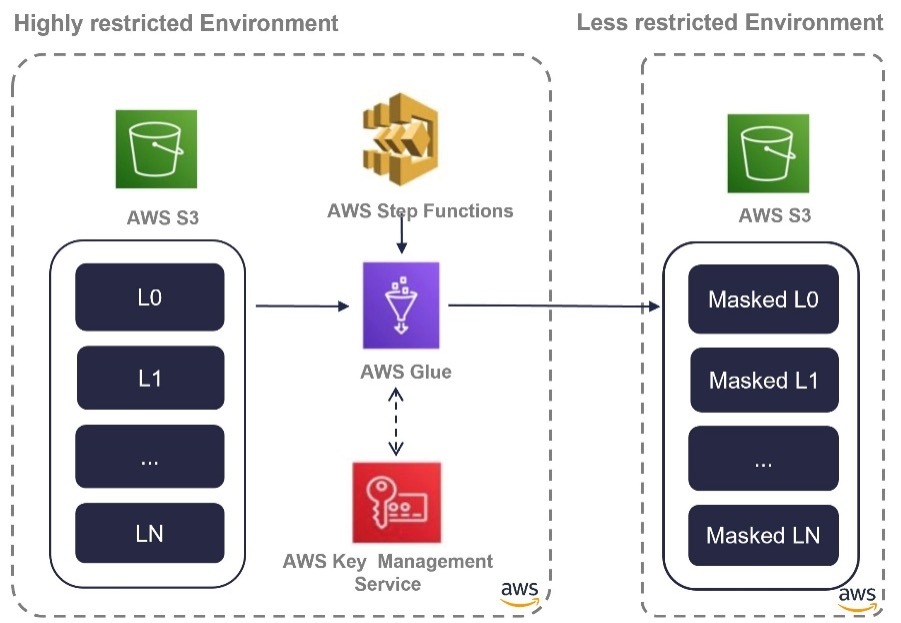
1. Classifying and Securing Sensitive Data
The first step focused on ensuring that personally identifiable information (PII) could be reliably identified, classified, and safeguarded within the data lake environment. This secure foundation established the strict boundaries needed to enforce governance and privacy requirements from the very start.
2. Encrypting and Masking with Format Preservation
Sensitive data was protected using format-preserving encryption (FPE), ensuring that PII remained secure while preserving referential integrity. This approach allowed encrypted values to maintain their original structure, enabling seamless use in downstream processes without exposing the actual information.
The Anonymization Key was stored in the highly restricted environment, and was not subjected to sharing or activity that could have compromised its security.
3. Enabling Safe Data Consumption
With PII securely masked and encrypted, developers and analysts were able to work with consistent, anonymized datasets in a development-ready environment. This ensured compliance while still supporting reliable analytics, enabling teams to conduct daily operations without risking sensitive information exposure.
The first step focused on ensuring that personally identifiable information (PII) could be reliably identified, classified, and safeguarded within the data lake environment. This secure foundation established the strict boundaries needed to enforce governance and privacy requirements from the very start.
Sensitive data was protected using format-preserving encryption (FPE), ensuring that PII remained secure while preserving referential integrity. This approach allowed encrypted values to maintain their original structure, enabling seamless use in downstream processes without exposing the actual information.
The Anonymization Key was stored in the highly restricted environment, and was not subjected to sharing or activity that could have compromised its security.
With PII securely masked and encrypted, developers and analysts were able to work with consistent, anonymized datasets in a development-ready environment. This ensured compliance while still supporting reliable analytics, enabling teams to conduct daily operations without risking sensitive information exposure.
Powering Digital Transformation through Data Platform Enablement
Data-driven organizations are three times more likely to report significant improvements in decision-making speed, helping them to respond faster to market changes
(Source: HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL)
Data Platforms can allow companies to realize cost savings of up to 15% through minimized redundancies, optimized resource utilization and streamlined processes.
(Source: McKinsey&Company)
Companies focusing on structured data management can improve data accuracy and consistency by 10-20% through centralized data platforms
(Source: McKinsey&Company)
Real-World Impact and Benefits
The project resulted in some key benefits:
| Operational Area | Before Implementation | After Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Data Privacy & Security | PII exposed to risks due to limited protection measures and fragmented governance. | Strong encryption and masking with format-preserving techniques ensured secure handling of sensitive data. |
| Compliance (GDPR & RTBF) | Difficulty managing GDPR requirements such as Right to Be Forgotten and data minimization. | Automated workflows enabled verifiable RTBF compliance and reduced overall data footprint. |
| Data Governance | Limited auditing, tagging, and visibility into where PII was stored or how it was used. | Comprehensive classification and tagging provided full traceability and improved governance. |
| Operational Efficiency | Developers and analysts relied on raw or duplicated PII, creating risks and inefficiencies. | Secure, anonymized datasets empowered teams to work productively without compromising privacy. |
| Business Risk | High exposure to compliance penalties, security breaches, and reputational damage. | Reduced compliance risks and strengthened customer trust through secure and scalable data processes. |
| Scalability | Legacy processes struggled to manage growing volumes of sensitive information. | Cloud-native, automated approach scaled seamlessly to handle massive datasets with consistent protection. |
Conclusions
With this solution in place, the client achieved a secure and scalable data ecosystem with a minimal data footprint, RTBF compliance, strong encryption and governance safeguarding sensitive data and scalability involving huge volumes of data without violating privacy laws. Ultimately, this architecture not only ensures regulatory compliance but also builds customer trust.